Counterfactual Delegation
Solidity framework for extending smart contracts
with counterfactual revocable-delegation
Counterfactual Delegation
Solidity framework for extending smart contracts
with counterfactual revocable-delegation
Scale the Web of Trust with Capabilities
- Library
- 1
- Caveat Enforcers
- 5+
- Of Opportunities
- 1,000's
Scalability. Security. Simplicity.
Access Controls for an Open Web3
Counterfactual Delegation
Delegate permissions to a third party without an on-chain transaction.
Bounded Permissions
Limit delegations by time, block, or any other on-chain condition using shared enforcers.
Readable Code using EIP712
Clearly express intent. And make it easy to verify the code and side-effects.
How it works
Delegations | Revocations | Enforcers

Off-Chain Signatures
Delegate smart contract permissions to friends, family, and/or third-parties using a Capabilities based EVM framework.

On-Chain Revocations
Revoke permissions at any time by submitting an on-chain transaction that invalidates the original delegation.

Composable Rules
Use a library of caveat-enforcers to create unique rules and conditions for delegations can be executed.
Easy To Understand Access Controls
The Delegatable Framework uses the EIP712 standard to create a human-readable and machine-verifiable signature. Limiting the risk of human error and malicious intent.
Human Readable | Express Intent
Users can more easily understand the permissions they are granting to a third-party. Seeing important information like the enforcer contract address, full capabilities, side-effects, expiration dates and more.
Machine Verifiable | Reduce Risk
Delegations, invocations and other transactions metadata can be verified by any machine. This allows for a more secure and reliable ecosystem. Providing opportunities to education and inform users about the risks of granting permissions.
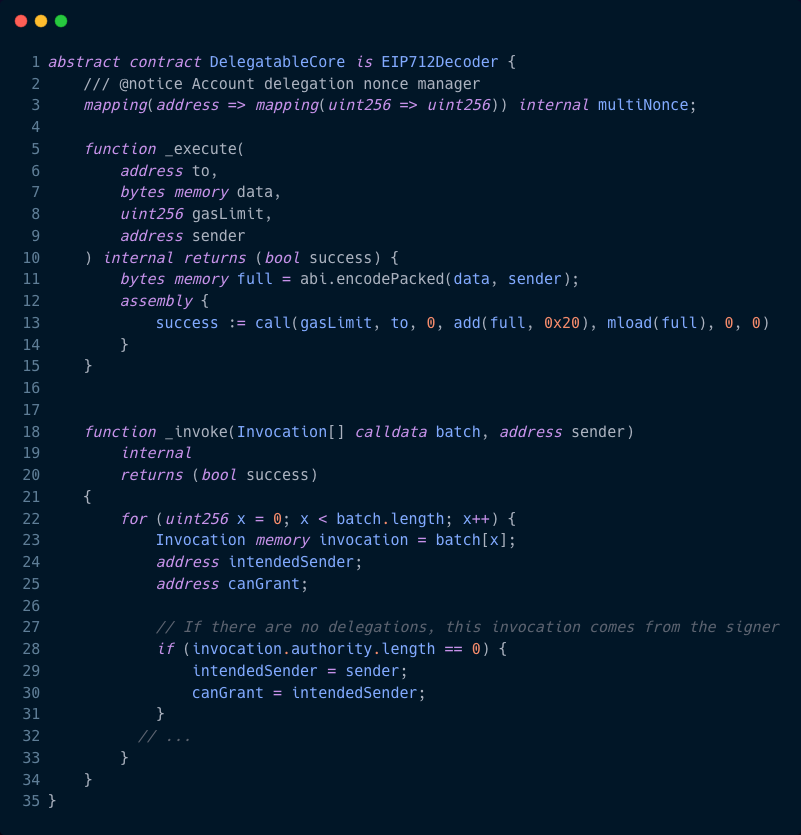
Layered Permissions + Chainable Signatures
The Delegatable Framework uses the EIP712 standard to create a human-readable and machine-verifiable signature. Limiting the risk of human error and malicious intent.
Grant permissions to any Wallet. Including Your own.
Stop using a single wallet for all your accounts.The Delegatable Framework enables Users to start using multiple wallets for different purposes, while still inheriting authority from a root Wallet.
Peer-to-Peer Access Controls. A Web of Trust.
Delegations can be re-delegated to other Wallets, without permission from the root Wallet. Enabling a new substrate of for a Web of Trust to emerge and more fluid peer-to-peer access controls for digital organizations.
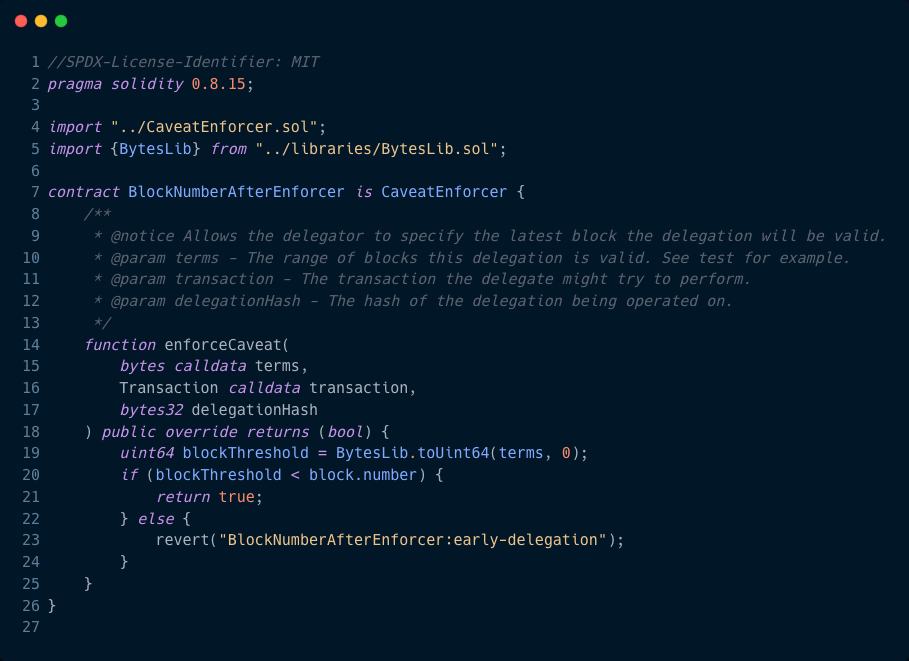
Caveat Enforcers
Bounded Access Controls for any Delegated On-Chain Permission
Timestamp Range
Use the `block.timestamp` global variable to enforce transaction execution periods; before, after, or between two timestamps.
Block Number Range
Use the `block.number` global variable to enforce transaction execution periods; before, after, or between two block numbers.
Nonce/Transaction Limits
Use a transaction log to enforce the maximum number of transactions per delegated address.
ERC20 Allowances
Use the `allowance` function to enforce the maximum amount of tokens that can be transferred from a delegated address.
Oracle Data
Use on-chain oracles to determine if a delegated permission can be executed. For example, if the price of ETH is above $1000.
If You Can Think It, You Can Build It
Write your own custom logic to enforce any permission you can think of. And compose them together to create complex permission systems.
Unlock Web3 at Human Scale with
Counterfactual Revocable Delegations
Explore the documentation to learn more about how to use
delegations, invocations, enforcers, revocations and more.
Delegations
Authorize any address to execute transactions on your Wallet's behalf. Enabling better private key management strategies and generalized capabilities access controls.
Enforcers
Limit the scope and duration of delegations using shared on-chain enforcers. Specifying conditions, like timestamp and blockNumber ranges, at the transaction signing level.
Invocations
Delegations can be invoked by any address, including other contracts. And custom transaction queues can be set, which means nonces are no longer a blocker.
Revocations
Delegations can be revoked at any time, using an on-chain revocation registry. This allows for granular, per-delegation, per-enforcer, per-invocation revocation.